Decomposition of Orientation Tensor Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
Usage
ot_eigen(x, scaled = FALSE, ...)
# S3 method for class 'spherical'
ot_eigen(x, scaled = FALSE, ...)
# S3 method for class 'ortensor'
ot_eigen(x, scaled = FALSE, ...)Arguments
- x
either an object of class
"Vec3","Line","Ray","Plane","Pair", or"Fault"where the rows are the observations and the columns are the coordinates, or an"ortensor"object.- scaled
logical. Whether the Eigenvectors should be scaled by the Eigenvalues (only effective if
xis in Cartesian coordinates).- ...
additional arguments passed to
ortensor()(ignored ifxis"ortensor"object).
See also
Other ortensor:
ortensor(),
strain_shape
Examples
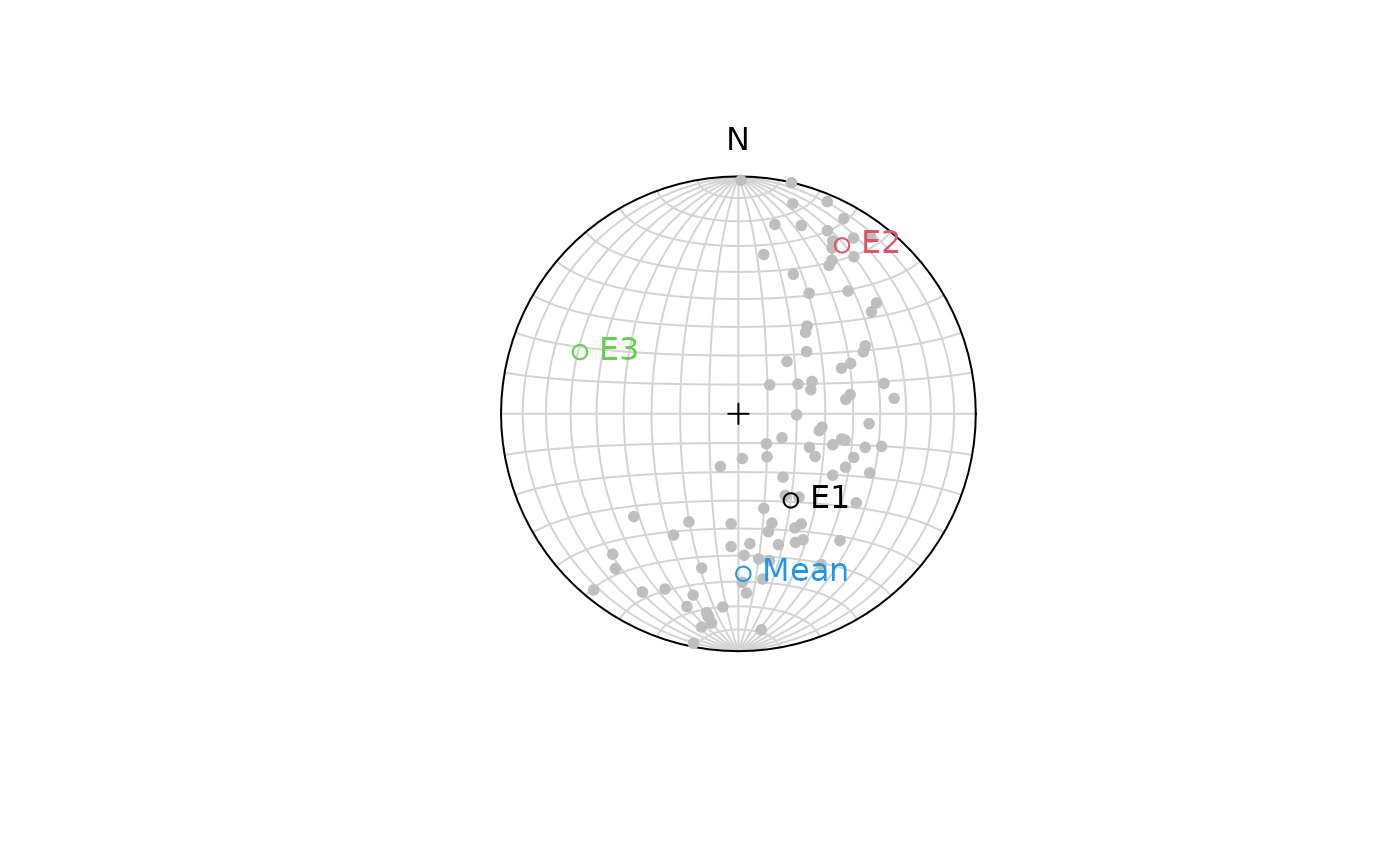
set.seed(20250411)
mu <- rvmf(n = 1)
x <- rfb(100, mu = mu, k = 1, A = diag(c(10, 0, 0)))
x_eigen <- ot_eigen(x)
x_eigen
#> eigen() decomposition
#> $values
#> [1] 0.48820354 0.46957691 0.04221956
#>
#> $vectors
#> Vector (Vec3) object (n = 3):
#> x y z
#> [1,] 0.6023891 -0.2756586 -0.7490926
#> [2,] 0.7557785 0.4988603 0.4241900
#> [3,] 0.2567609 -0.8216756 0.5088449
#>
plot(x, col = "grey")
points(mu, col = 4)
text(mu, labels = "Mean", col = 4, pos = 4)
points(x_eigen$vectors, col = c(1, 2, 3))
text(x_eigen$vectors, col = c(1, 2, 3), labels = c("E1", "E2", "E3"), pos = 4)