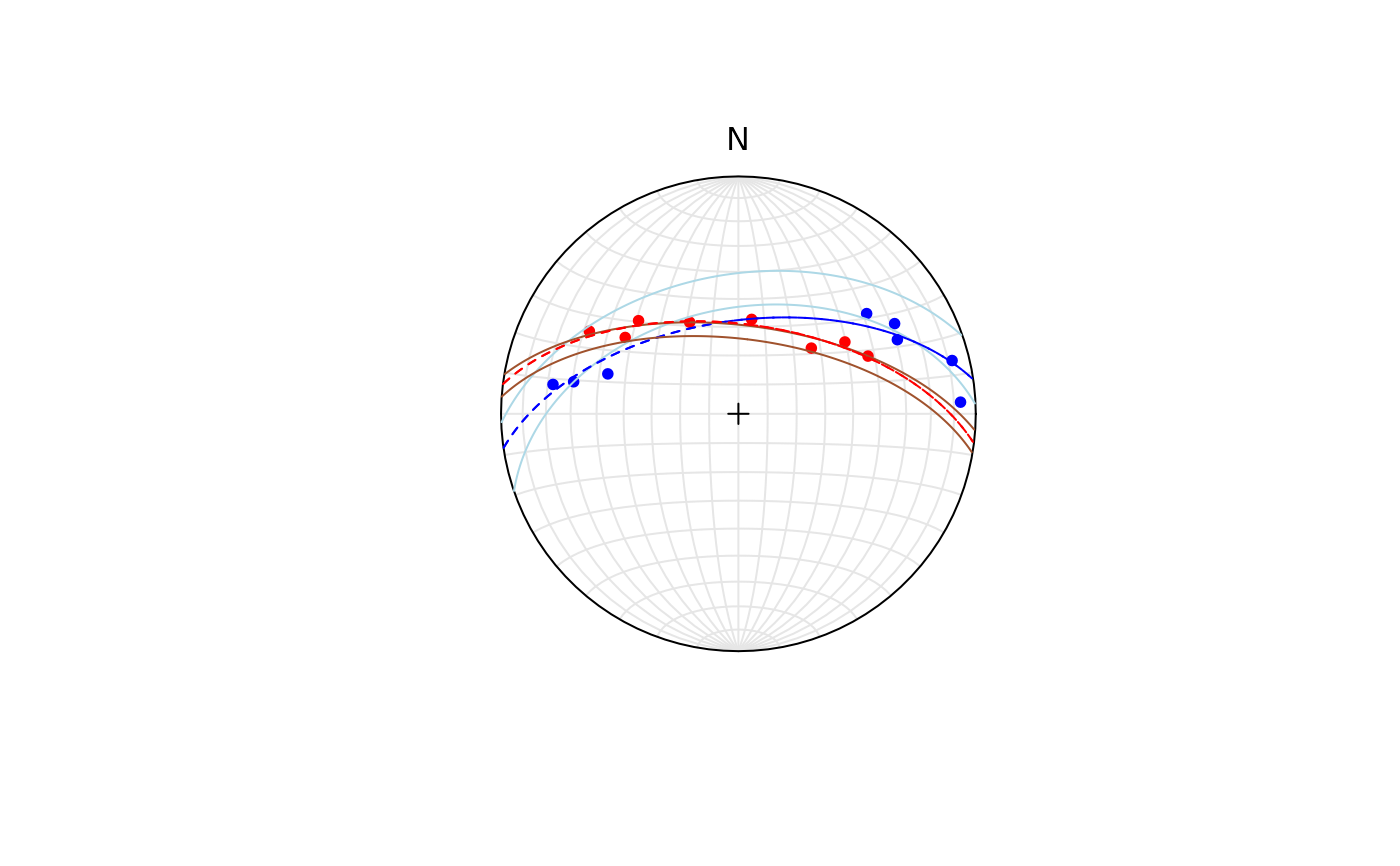
Least-square fit of small and great circles to spherically projected data
Source:R/best_pole.R
best_fit_plane.RdFinds the best small and great circles using the algorithm by Gray et al. (1980)
Value
list
list. axis_c is the axis of the small-circle cone, axis_g is the axis of the great-circle,
cone_angle is the halfapical angle of the cone, r_* is the residual
References
Gray, N.H., Geiser, P.A., Geiser, J.R. (1980). On the least-square fit of small and great circles to spherically projected data. Mathematical Geology, Vol. 12, No. 3, 1980.
Examples
data("gray_example")
gray_example1 <- gray_example
gray_example1$dipdir = gray_example1$Strike + 90
gray_example1$dip = gray_example1$Dip
gray_example1$id = seq_along(gray_example1$dip)
gray_cleavage <- subset(gray_example1, Type == "Cleavage")
gray_bedding <- subset(gray_example1, Type == "Bedding")
test_clea <- Plane(gray_cleavage$dipdir, gray_cleavage$dip)
test_bedd <- Plane(gray_bedding$dipdir, gray_bedding$dip)
best_clea <- best_fit_plane(test_clea)
best_bedd <- best_fit_plane(test_bedd)
stereoplot()
points(test_clea, col = "blue")
points(test_bedd, col = "red")
lines(best_clea$axis_c, best_clea$cone_angle, col = "lightblue")
lines(best_clea$axis_g, 90, lty = 2, col = "blue")
lines(best_bedd$axis_c, best_bedd$cone_angle, col = "sienna")
lines(best_bedd$axis_g, 90, lty = 2, col = "red")